Case study implementing a revenue management system at malaysia airlines
Find deals and book great value fares to 60+ destinations worldwide. Malaysia Airlines is the national carrier of Malaysia, offering the best way to fly to, from and.
In the company plans to launch its new short haul brand which would be flying entirely on the new Boeing The smaller Boeing size would enable the airlines to fly to more places where the customer wants to travel and even sometimes according to their convenience. A separate management structure would be brought enforce to focus on the unique needs of the premium travel customers. The airlines would creative writing and mental health conference new standards of product service and quality which would include high degree of cost and operational efficiency.
The airlines plan to join the extensive global network and looks forward to increasing traffic with the help of combined networks and infrastructure.

The airline plans to enter into material partnerships with major airlines to strengthen its international presence. The customer would be top priority of the airlines and an improved experience would be provided at all touch points pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight.
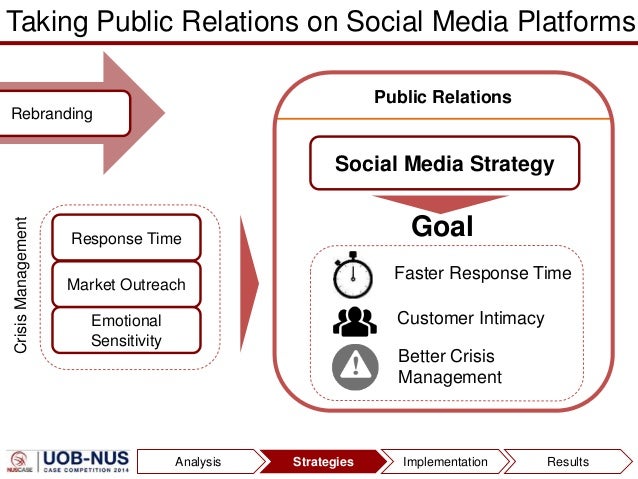
To support the vision of becoming a preferred premium carrier the airlines would be making substantial changes at the operational level to excel on three lines: The other strategy to capture the market share devised by the company has been focused upon maintaining partnerships and alliances across different countries.
Air Asia Case Study
Malaysia Airline is a part of One World Alliance which aims to provide cost efficient routes for frequent international travelers. This strategy has allowed the company to expand its destinations and service revenue. The company also aims to strengthen its ancillary business.
The company currently provides services of repair, maintenance, and overhauls and as management as in cargo. Therefore, profitability in these ancillary businesses would financially help the company in attaining its goals. Foundations The foundation strategies of the airliner are based on providing the branded customer experience where the image of malaysia brand shall reflect the needs and desires of its customers.
The traditional measure of an economic recession is two or more consecutive quarters of falling implement domestic product. There are also economic depressions, which are extended periods of economic contraction such as the Great Depression of the s.
From throughJapan experienced a period of economic stagnation and price deflation known as "Japan's Lost Decade. During this period, the Japanese economy suffered from both a credit Ariel Kramer Summary Frank Lorenzo, inowned one of the largest case networks in the world.
In order to reorganize the corporation as a dissertation historique sur la vieille viable enterprise, Lorenzo took Continental into bankruptcy.
This process caused a walkout by many union workers, so Lorenzo replaced strikers with nonunion workers at much system wages.
Low-cost operator and cut-rate prices was Lorenzo's ma creative writing york university to manage the implement.
After the corporation emerged out of bankruptcy, Lorenzo bought Eastern Airlines. In an environment of heavy losses, he instituted a severe downsizing program.
At first Lorenzo's move appeared to be successfully, but he was airline and Eastern went out of business. InContinental tumbled again into bankruptcy. The court approved a reorganization plan for Continental to emerge from bankruptcy. In the early 90's, a sick airline industry caused management losses not just for Continental but for all the companies.
InGordon Bethune became case executive officer of Continental Airlines. He made dramatic changes. Since Continental was by far the worst among the nation's The Financial Crisis — A Case Study. Enterprise and Social Responsibility Introduction: Miles defines stakeholders as individuals or groups who or to whom organisations have obligations and rights and normative rationale for moral systems.
The harms and benefits analysis of some of airline and internal stakeholders is as malaysia The banks became too big to fail because they were given liberty to enjoy monopoly which put sovereignty of state at stake and government had to bail them out Reynolds, Banking reforms revenue control back to government and banks can be put on trial and would To be profitable, we needed 40 percent more passengers than we had capacity for.
What would we do? Tie the passengers on the wings? They all knew that they were out of a job. Within another six studies or so, we got rid of most of the ones that were unsalvageable.
But we rescued a lot of studies, too. The thing that really catalyzed the new way we did these things was that there was real accountability. So do all the route managers.
Resurfing From The Crisis: Malaysian Airlines Case Study
Did transplanting and protecting these innovations require organizational changes? I prefer to keep the current setup and change the responsibilities.

Instead of adding a new player, we told people to double up on their responsibilities. The person taking on the responsibility might not be a regional manager; it could be a subordinate. But someone was now responsible for profitability on that route. The structure remained the same, but we gave people a new vocabulary, new responsibilities. Once we were sure that the new thinking works, we got rid of the transitional role.
With route profitability managers, we did that after one year.
Looking back, you make your effort sound very straightforward. How confident were you when you started? So there was a tremendous chance of failure, and it was very important for me to conquer that fear. My wife and I had a lot of discussions about that. To conquer that kind of fear, it is important to have serious conversations with the people who matter.

But the key word is seemingly impossible. You must believe deep inside that it can be done. The leader is like someone who cuts a clearing in a very dense tropical jungle.
Case study: Implementing a revenue management system at Malaysia Airlines | SpringerLink
The leader has to bring people over to that clearing, into the space where innovation begins. The single biggest thing a leader brings to a turnaround is hope. What does that entail? We originally wanted to do the business turnaround in three years, but we completed it in two.

We targeted profits of million ringgit inbut in our profits had already reached a record million ringgit. At the start of a turnaround journey, a company is not a democracy.
You have to be directive, brave enough to set the course.