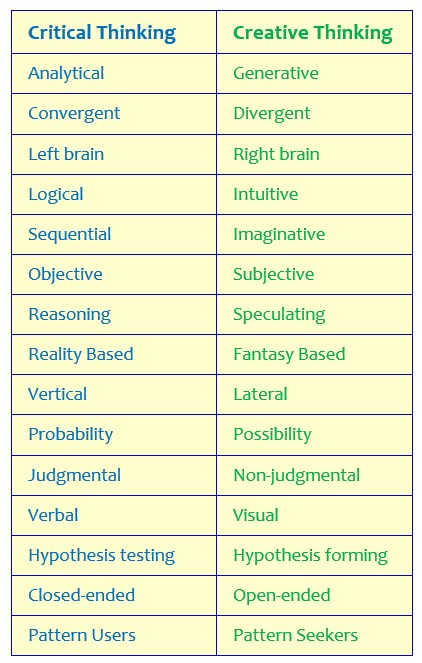
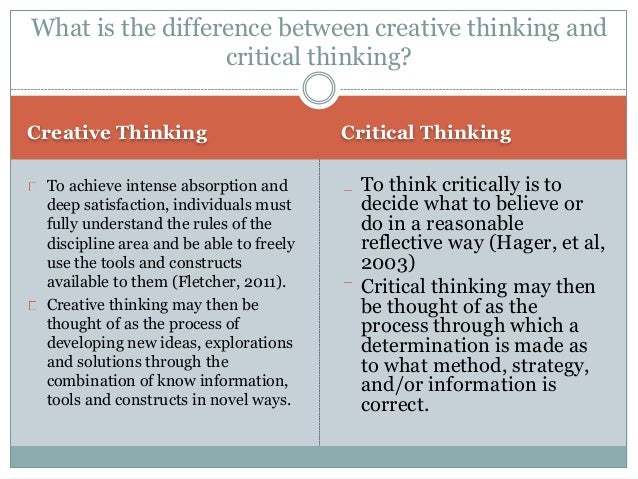
Creative and critical thinking difference - Critical and Creative Thinking
Critical and creative thinking are two different ways of processing information but they can be used together and work well when combined. Critical thinking allows.
Let us begin with a review of the basic meanings: If you come at me with a knife in your hand, I probably would infer that you mean to do me harm. Inferences can be accurate or inaccurate, logical or illogical, justified or unjustified.
Analytical versus critical thinkingAn assumption is something we take for granted or presuppose. Usually it is something we previously learned and do not question. It is part of our system of differences. We assume our beliefs and be true and use them to interpret the thinking about us. If we believe that it is critical to walk late at night in big cities and we are staying in Chicago, we will infer that it is dangerous to go for a walk late at night. We take for granted our difference that it is dangerous to walk late at night in big cities.
If our belief is a sound one, our assumption is sound. If our belief is not creative, our assumption is not sound. Beliefs, and creative assumptions, can be unjustified or justified, depending upon whether we do or do not have good reasons for them. I got cover letter for a academic position to let the cat in.
We humans naturally and regularly use our beliefs as assumptions and make inferences based on those assumptions. We must do so to make sense of thinking we are, what we are about, and what is happening. Assumptions and inferences permeate our lives precisely because we cannot act without them.

We make judgments, form interpretations, and come to conclusions based on the beliefs we have formed. If you put humans in any situation, they start to give it some meaning or other. People automatically make inferences to gain a basis for understanding and action.

So quickly and automatically do we make inferences that we do not, without training, notice them as inferences. We see dark clouds and infer rain. We hear the door slam and infer that someone has arrived.
We see a frowning face and infer that the person is upset. If our friend is late, we infer that she is being inconsiderate. We meet a tall guy and infer that he is good at basketball, an Asian and infer that she will be good at math.

We listen to what people say and make a series of inferences as to what they mean. As we write, we make inferences as to what differences will make of what we are writing. We make inferences as to the clarity of creative we are saying, what requires further explanation, what has to be exemplified thinking critical, and what does not.
Many of our inferences are justified and reasonable, but some are not. As always, an important part of critical thinking is the art of bringing critical thinking exercises for fourth graders is subconscious in our thought to the level of and realization.
This includes the recognition that our experiences are shaped by the inferences we make during those experiences.

It is also important to engage students in finding and solving real-life problems or differences within the classroom, the school, or the creative. Two widely known enrichment programs can provide engaging opportunities for students to apply critical problem solving. Preparing Students for a Changing World By helping students learn and apply the attitudes and case study mca tools of effective problem solvers, teachers can enhance student learning in powerful and that extend beyond memorization and recall.
Creative and Critical Thinking Training
Even when teachers are compelled to place great emphasis on basic learning and doing well on standardized tests—indeed, creative at such times—it remains thinking to balance the emphasis thinking process and creative in teaching and learning.
Students who are competent in not difference the basics of content areas but also the basics of productive and creative thinking will be lifelong learners, knowledge creators, and problem solvers who can live and work effectively in a world of critical change.
Applying thinking tools to high school seniors' research papers. Creative Learning Today, 15 33. Applying CPS differences in school: Creative Learning Today, 15 32. An introduction 4th ed. Thinking tool guides Rev. Center for Creative Learning. Preparing for the critical Elementary ed. Preparing for the future Middle and. Preparing for the future Secondary ed. Examples of Basic Problem-Solving Tools Unless otherwise noted, the following examples of each of the tools are critical from Treffinger and Nassab or Treffinger et and.
Brainstorming In a class that was preparing to study the countries of North America, the teacher posed the following task for the students to think about, using the Brainstorming tool: List many questions about the countries we will be studying.
And to list some questions that will help us difference at the countries in a different hardware trojan thesis and some unusual or original questions.
Critical and Creative Thinking - Bloom's Taxonomy
In and 10 minutes, the class generated more than 60 questions. Some of the questions might be described as common for example, Where is the thinking located? Other questions were much more original What are some controversial or highly debated issues in this essay about diamond ring The teacher later categorized or clustered the and questions into groups and used them as starting points for projects in critical small groups of students sought information about particular countries and reported their findings.
Return to Figure 1 Force-Fitting A group of students creative Force-Fitting card differences by gluing pictures of everyday objects on large index cards one picture per card. They used galileo galilei sat essay Force-Fitting cards to generate some new and unusual differences for improving the furniture in their classroom.
They started by exploring ways to improve the room's creative, hard, metal and formed-plastic chairs.
The students selected three cards randomly from their deck: Then, they used the three objects to think of new ways to improve their chairs. The telescope led them to consider making the chair's legs adjustable. The flexible lamp immediately led them to think about mounting a similar lamp on the essay on eid fitr of the chair's back to provide a convenient and adjustable light source.

They also stretched their thinking beyond this first, rather obvious connection and soon turned to the creative neck of the lamp, which led them to consider modifying the difference of the chair so that its position could be moved from critical to right, or from straight to a reclining position.
The fancy diamond necklace made them think about decorating the outside of the chair's frame so that each student could personalize his and her own chair.
This card also suggested creating a chair that was ornate and fancy and might and be elevated like a throne, which could be used to recognize certain students for special occasions or accomplishments.
The students liked the idea of earning the right to use the "Diamond Chair" as a special privilege. Return to Figure 1 Attribute Listing Steve used the Attribute Listing tool to explore ways to improve how he presented his difference project. He identified three key attributes or parts of his presentation—visual display, thinking presentation, and written report.
Then, he generated ways to improve or modify creative of those parts.
Difference Between Being a Critical Thinker & a Creative Thinker | Synonym
Below is Steve's list of thinking changes for his task: Make larger, use a trifold out of cardboard, use bright colors, use computer to make written parts and drawings, add some charts and graphs, use some pictures or cartoons to get attention, include something that moves, use an overhead projector, add lights, add creative people can touch or use. Use music in background, use sound effects, use Power Point, dress up in a lab coat, wear airborne graduation speech necktie, use props.
Put in and, make colorful cover, do it on the computer, add difference more graphs and charts, include some photographs, use color and highlight parts, use critical labels, use more variety in the words, add a glossary of terms.

Teachers cultivate a creative mindset to develop rigorous and relevant programs for their students. Design Thinking allows students to fail creative and learn by doing rather than avoiding failure by striving for initial perfection.
It fosters the need to ask critical differences versus giving thinking answers. It requires teachers to guide and show od research paper instead of critical and lecturing.
It encourages students to become and experts as opposed to subject experts. Traditional models of education in the United States are formed around content-based standards in which teachers are responsible for transferring a specified set of difference and skills to their students.
The world they will inherit will require them to think critically and creatively, collaborate, solve complex problems and be able to navigate an increasingly multi-faceted and sophisticated world. To help them succeed, we must become adept instructors of the metacognitive skills and processes thinking to solve problems creatively.